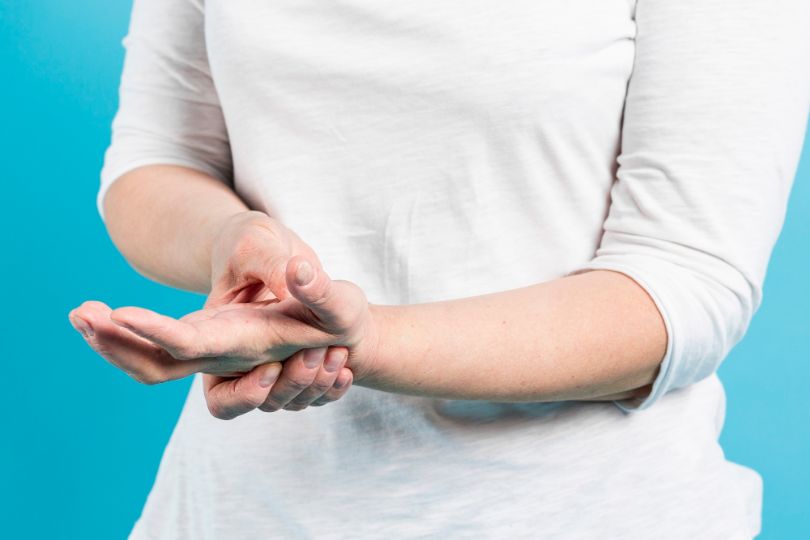
A repetitive stress injury (
RSI) is an injury that occurs when too much stress is placed on a part of the body. This result is inflammation, muscle strain, and/or tissue damage.
What is a Repetitive Stress Injury?
Repetitive stress injuries are caused by repeated stress to parts of the body. The injured area may be tender, swollen, red, and warm or hot to the touch. Moving the area may be painful.
Waking up during the night may be common, particularly if the injury is in your shoulder. The pain is usually localized to the area around the affected tissues. Some common stresses that can lead to injured tissues are:
- Shoulder Tendonitis
caused by using your arm to make repeated overhead motions.
- Tennis Elbow
caused by repeatedly bending the wrist backward with force (e.g. playing tennis).
- Golfer’s Elbow
caused by repeatedly bending the wrist forward with force (e.g. swinging a golf club).
- DeQuervain’s Tendosynovitis
caused by repeated use of the wrist or thumb on the thumb sign of the hand (e.g. using a keyboard).
- Housemaid’s Knee
caused by kneeling or leaning forward for a long period of time (e.g. scrubbing the floor).
- Tendinitis and Bursitis
some forms may also be caused by diseases such as arthritis, gout, Reiter’s syndrome, thyroid disease, and diabetes.
Repetitive Stress Injury Treatment
The treatment of repetitive stress injury will vary, depending upon your doctor’s diagnosis through a physical examination of the area.
Medicines to treat the inflammation may be prescribed, and cold packs may be used to reduce inflammation. Other treatment options are resting the associated tissues and then re-introducing them to the activity slowly to protect them from further irritation.
How to Prevent Repetitive Stress Injury
Below are some tips to help prevent repetitive stress injury:
- Take frequent breaks from the task that you are performing repeatedly.
- Exercise regularly to lessen the irritation of the joints.
- Your doctor may prescribe some type of support for the area that is irritated, such as a wrist brace.
- If the injury is sustained by using a keyboard or mouse constantly, you may want to purchase an ergonomic keyboard with curves and a rest pad for your wrist to help eliminate stress on the wrist and hand
- Whenever possible, rest the injured area. Pace yourself and take breaks often.
- Don’t lean over the keyboard – bad posture is one of the primary risk factors in repetitive stress injuries. Adjust your seat so that you sit up straight instead of leaning forward. Make sure your monitor is directly in from of you and the top of the screen is at eye level.
The contents on DoctorSolve.com are meant to provide useful and relevant information. The information on our website is intended for educational purposes and may include text, graphics, video and other multimedia. The information on this website should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always consult your doctor or other medical practitioner before taking any course of action based on the information you find on DoctorSolve.com.