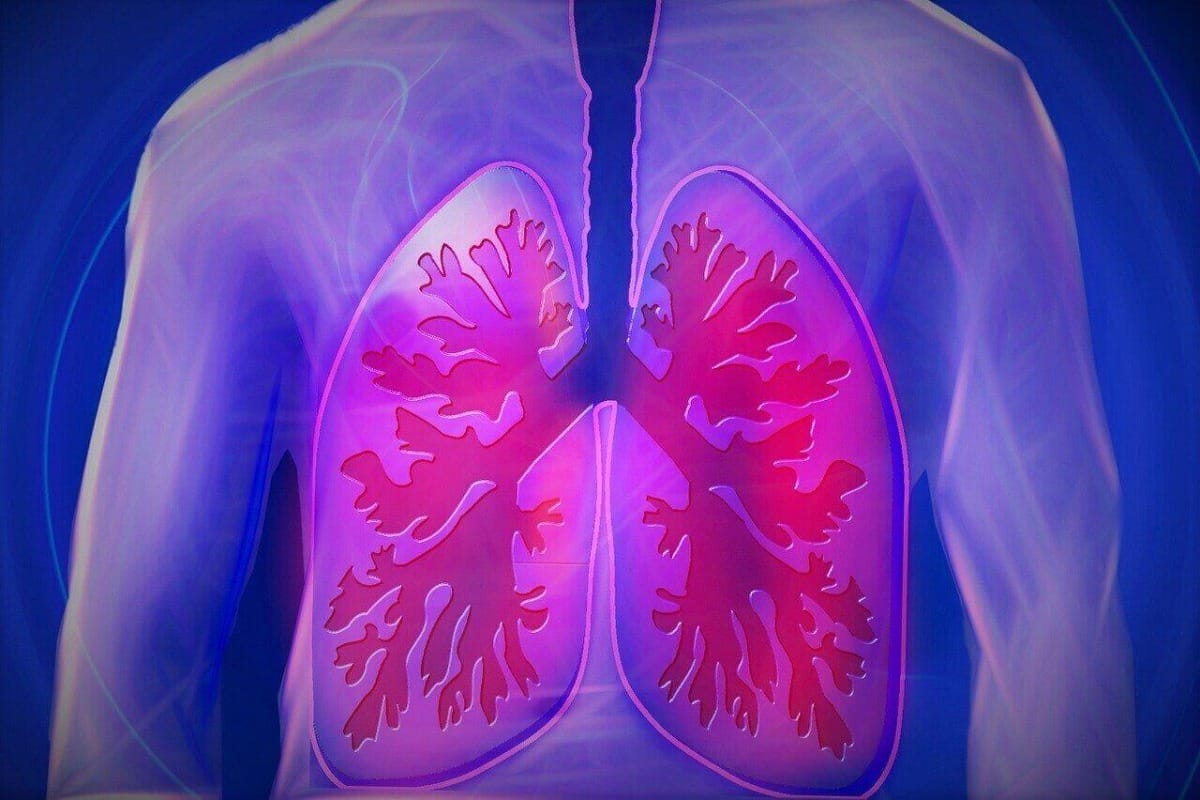
Pneumonia is an infection that is often characterized by an inflammation in the alveoli. The alveoli are tiny sacs in the lungs that are responsible for gas exchange which is a vital part of breathing. These sacs become infected when pneumonia-causing germs are breathed in and begin accumulating in the lungs. This infection can be caused by various types of fungi, parasites, bacteria, or viruses. Some of these pathogens are found in hospitals. About 10% of all hospital infections, including pneumonia, are caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa [1].
Pseudomonas aeruginosa treatment is extremely difficult because it is very resistant to antibiotics. Many cases of pneumonia caused by pseudomonas aeruginosa shift from acute cases to chronic cases due to a specific interaction with calcium. The environment around the pathogen determines if the condition will switch from an acute stage with a high growth rate or a chronic state with increased tolerance and persistence. It has recently been discovered that calcium concentration in the environment transmits a signal into the cell that triggers the switch. Generally, hospital infections which lead to pneumonia can be quite severe and many of these infections are a result of patients surviving with the aid of ventilators.
A study conducted by Fagon et al. assessed the exposure of risk in patients with pneumonia caused by hospital infections. The study concluded that the mortality rate was considerably higher due to hospital infections and it “prolonged the stay [of the patient] in the intensive care unit” [2].
Sources: [1] "Calcium induces chronic lung infections." Science Daily. 24 October 2016. Retrieved from www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/10/161024131112.htm [2] Fagon, Jean-Yves, et al. "Nosocomial pneumonia in ventilated patients: a cohort study evaluating attributable mortality and hospital stay." The American journal of medicine 94.3: 281-288. Accessed 25th October 2016
Also Read
Shortage of Drugs Worrying Anaesthesiologists
US Drug Spending Is Increasing
Symptoms and Causes of Cystitis
Doxycycline Uses to Treat Bacterial Infections (Pneumonia & Other Respiratory Infections)
Minocycline for Bacterial Infection Stops The Infection In It’s Track